Litter, defined in its broadest terms, includes any solid material present in the environment that was . It may have arrived there from an accidental spillage, as debris washed ashore, or because of the of industrial waste.
How some types of litter enter and travel through the environment cannot be traced. Litter breaks down beyond recognition, identifying marks such as branding wear away and rivers can transport it far from where it originated. But some litter has clear sources and pathways, discernible from its function and packaging labels, from which the brand that made the item can be easily identified.
The community interest company created an app for people to record the litter they find and remove. We used it to map the location, materials, type and, where possible, brands of 43,187 items of litter collected across the UK in 2020. Our research was recently published in the .
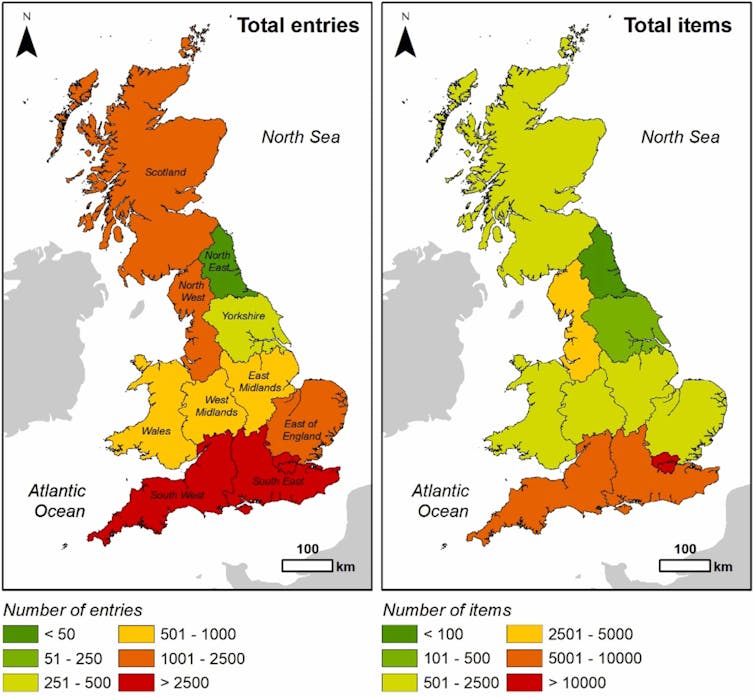
App users submitted the litter they found throughout the UK. , Author provided.
Plastic was the most common material recorded, accounting for 63.1% of all items. Metal was second (14.3%), followed by composite materials (pieces of litter made from more than one material, like Tetrapak cartons) at 11.6%. Bottles, lids, straws and other items from the drinks industry made up 33.6% of the total, of which metal cans were the most common.
Our citizen scientists identified brands for 16,751 items (38.8% of the total), with 50% of these belonging to just ten brands. The Coca-Cola Company was the most frequently identified brand (11.9% of branded litter), followed by Anheuser-Busch InBev (7.4%) and PepsiCo (6.9%). The top three brands were all drinks manufacturers.
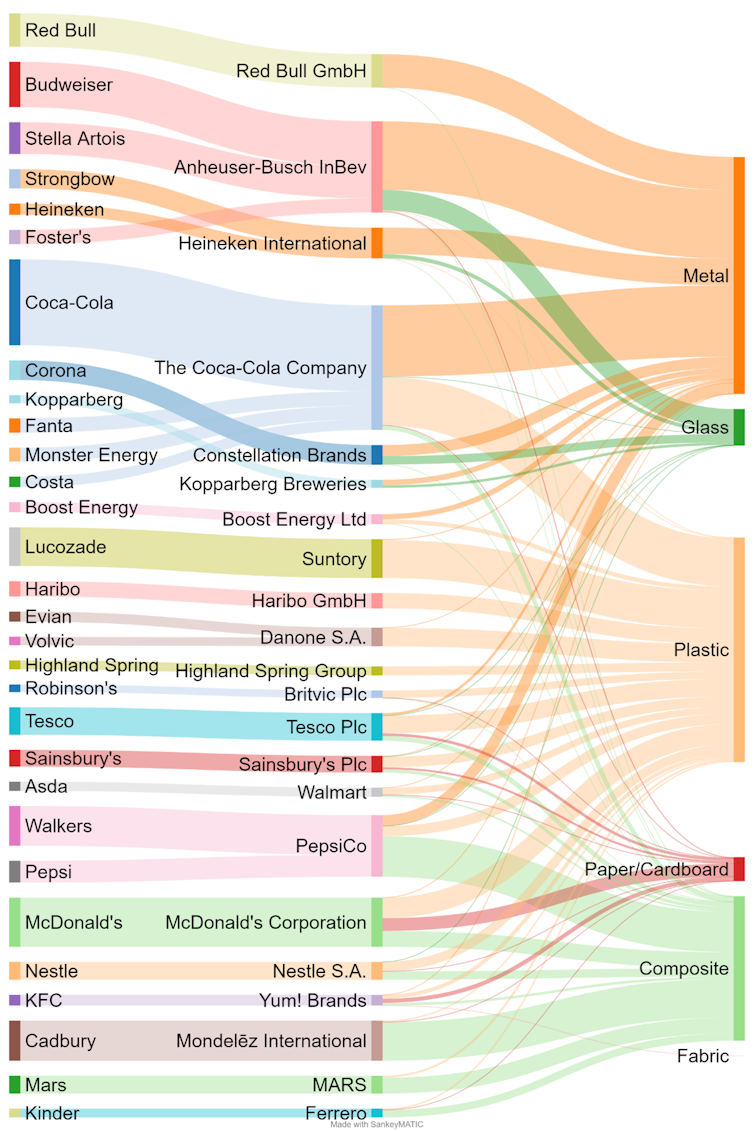
Despite taking up most space in the statements of packaging manufacturers, plastic comprised a third of total litter found. , Author provided.
Plastic policies
Surprisingly, our findings do not vindicate one of the EU’s most important orders on litter: the 2019 . This identified the based on beach surveys around Europe, and legislated to reduce their production and sale in the EU while the UK was still a member.
These ten items, which include cotton buds, plastic bags and plastic bottles, were not all common in our results, which came from sampling inland areas as well as some beaches. Though this directive applies to the whole of the EU, we suspect its focus on coastal environments alone does not accurately reflect the nature of most litter found across Europe.
Throughout the 2020s, the UK government and its devolved powers will introduce or reform legislation to tackle litter. These include a (introduced in April 2022), a tax on the production of plastic packaging containing less than 30% recycled plastic, a for drink containers (limited to plastic containers only ) and which will make packaging producers pay for action including litter picking and education campaigns. Over the same decade, the top ten companies identified by our study plan to change the materials they use in their packaging.
Our analysis of these corporate and legislative policies concluded that they disproportionately favour solutions based on recycling, with little consideration of how to reduce waste and allow people to reuse items. This approach fails to address plastic pollution’s root cause: selling things people don’t really need.
Dr Tom Stanton and colleagues share their findings of a study that looked at 40,000 pieces of litter .
Read the article in full .
